Nowadays, many people rely on the internet and social media for information, increasing the likelihood of getting unverified information. Given the large number of people consuming news online nowadays, the internet is the easiest and fastest medium for spreading false news.
False news has become a global problem, gaining traction in the US since the 2016 election. Spreading fake news can have far-reaching consequences on people, from impacting the news consumers’ mental health to inflicting physical damage. About 64% of US adults think false information can easily be confused with facts. Check out these shocking fake news statistics in 2025 to explore the facts about misinformation you probably never knew until now.
Key Fake News Statistics
General False News Statistics
1. 53% of Americans believe they see false and deceptive news every day online.
2. 50% of American bookworms come across fake news on social media once a day.
3. 3 out of 10 Americans believe in misinformation.
4. 23 % of Americans believe they have shared cooked-up stories unknowingly.
5. Less than half of the news on the internet is safe.
6. 16% of Older adult Americans believe they have shared fake news and found out later that it was fake.
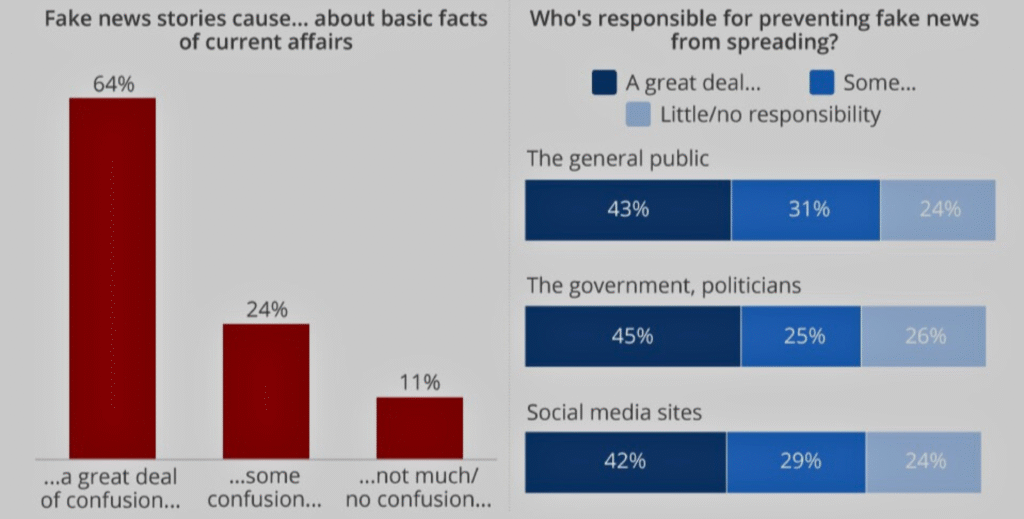
7. According to research,64% of older American adults say that false news can confuse them about basic facts and current issues.
8. As of 2017, 32% of Americans believe they have seen false political news online.
9. 87% of worldwide citizens support education in the identification of fake news.
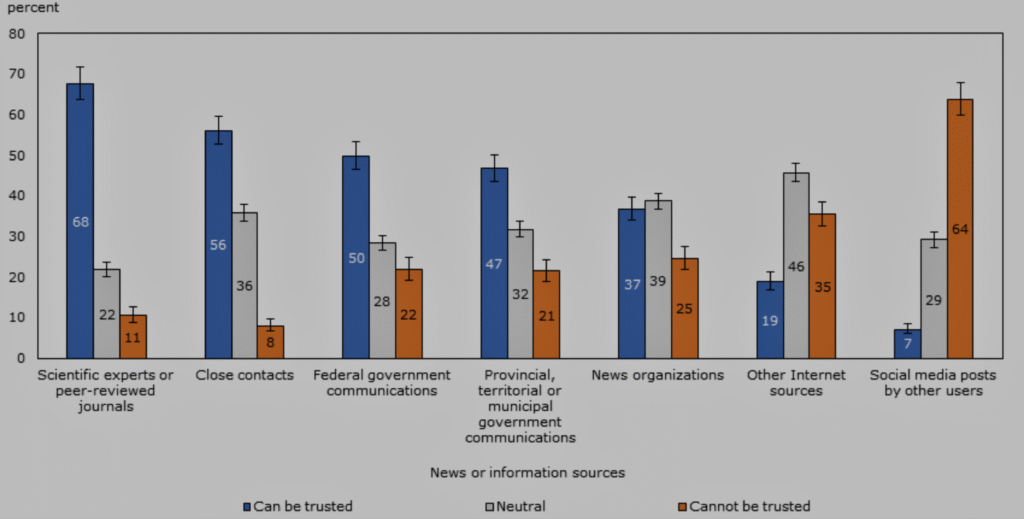
10. 44% of news readers say they can’t trust local news sources.
11. 80% of US citizens, especially adults, have consumed fake news about the COVID-19 pandemic.
12. According to a survey, 80% of students in 2016 believed that sponsored content articles were the main stories.
13. Up to 65% of people seek opinions they know by using the internet for answers, while 3% live in truth.
14. About 58% believe seeking opinions from known sources is better than the regular ones in catching fake news sources.
15. As many as 63% of people identify fake news, but 41% of the average person can.
16. Up to 49% of Americans using the media encounter false news.
17. About 78% of people who use the internet worldwide are concerned about their privacy because of the continuous spread of fake news.
18. With fake news dominating the internet, only 35% now trust information from the net.
Statistics on How People Perceive Fake News
19. Because of fake news and distrust in the media, about 40% no longer trust the media for information.
20. Based on demography, older Americans now believe that mainstream media gives false news.
21. With the spread of false news, pages like Facebook have taken action by removing millions of fake news stories, especially about the COVID-19 pandemic, with false information.
22. According to 25000 thousand number of people interviewed, it is said that about 86% of online users worldwide believe they have been exposed to fake news.
23. Nine in ten of the 86% at first believed that the news was factual.
24. About 67% of people on Facebook come across fake news, and some other social media pages, like websites, have 65% fake news, YouTube 56%, and television 51%.
25. As many as 87% of people believe that the internet is becoming worse with fake news, while the negative impact on politics in their countries is 83%.
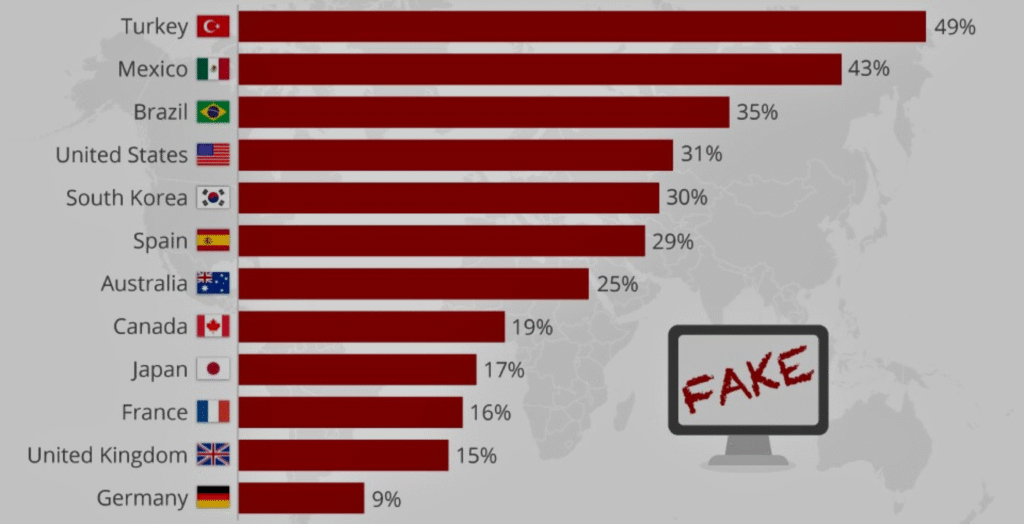
26. The sources of fake news with many economic views and also responsible for its unruly news on the internet are the US (35%), Russia (12%), and China (9%).
27. Based on variation, it is varied that Canadians are 59% turkeys 59% and Americans are 57%.
28. In contrast, those living in Hong Kong, 39%, Japan 38%, and India 29% are likely to blame China.
29. Of the actors responsible for spreading fake news, 81% are online trolls, and 82% are social media platforms.
30. In government, we have 68% foreign, 71% social media,75% regular internet users, and 72% play a part in the spread of fake news.
What Amount of Information on the Internet Is Real in 2025?
31. The consensus amount that falls under the influence of government is 17%, and the internet users are 16%, while 12% think that organizations should have a role. Dictating the precise amount of accurate information online in 2025 is very difficult due to the growing size of content and the independent nature of truth in many situations. Thus, only 50% of some online information may be factual. However, many key points can be measured. The following statistics are pointers to how reliable online information is in 2025;
32. Less of the information in the media is reliable. According to the Center for Statistics Office, 62% of data on the net today is untrustworthy. Based on a survey by the Center for Communication Policy, 47.3% of the information in the media today is fake and variable. Most false news was found in online sources like political blogs, Wikipedia, and social media. Most false news was also found on social media, where people participated the most.
33. The number of Americans who believed in false news. The rise of false news is becoming significant, especially in this period of information from the media. According to statistics, 30% of Americans believe in half-truths, while 70% separate them from the actual truth.
34. Out of ten Americans, only three believe in false news. Based on a study by YouGov, 7 in 10 Americans can identify fake and real news. The study emphasized that a considerable number of Americans who believed in fake news were 41% of the younger ones between 18-34 years old. Only 44% of older Americans over 65 years old knew the real news and fake news when they saw them. So, in evaluation, 37% of adults fall for fake news, while 38% of those aged 50-64 fall for fake news.
How Frequently Do You See Fake News?

35. About 84% support removing fake news posts or tweets on social media and video-sharing sites. 85% and 87% of the population wanted better education on identifying fake news.
36. 53% of Americans say they come across half-truths online daily. In America, 7 in 10 people believe they have encountered misinformation in a week. Thus, two-thirds of the older adults said they encounter false news every day. Source YouGov.
37. 86% of global citizens have been exposed to fake news. The increasing rate of cybercrimes is making people not trust news on the internet, and about 26% of worldwide citizens do not trust internet news again.
38. 44% of worldwide news clients have received false news. Reading fake news online every day can be very frustrating because it is becoming an industry on its own. Individuals are paid to write sensational stories, and the internet spreads fake news.
39. On the internet today, where news reach is unlimited, false news has arisen as a risk, and 90% of people have been impacted globally.
40. Around 86% of people worldwide have been exposed to fake news. One in four people (26% of the global population) do not trust the internet today due to the rate of fake news on social media. This number has been increasing yearly.
41. About 32% of US adults trust the media news. Greece recorded the lowest level of news in the media. Only 19% of the country’s abode trusts the news media. Meanwhile, Finland has the highest trust in news media, with 56% of adults trusting the media. In comparison, just 33% in the UK trust the press.
42. Around 49% of people believed to have been forced to reveal personal information online due to distrust.
Fake News on Social Networks Today
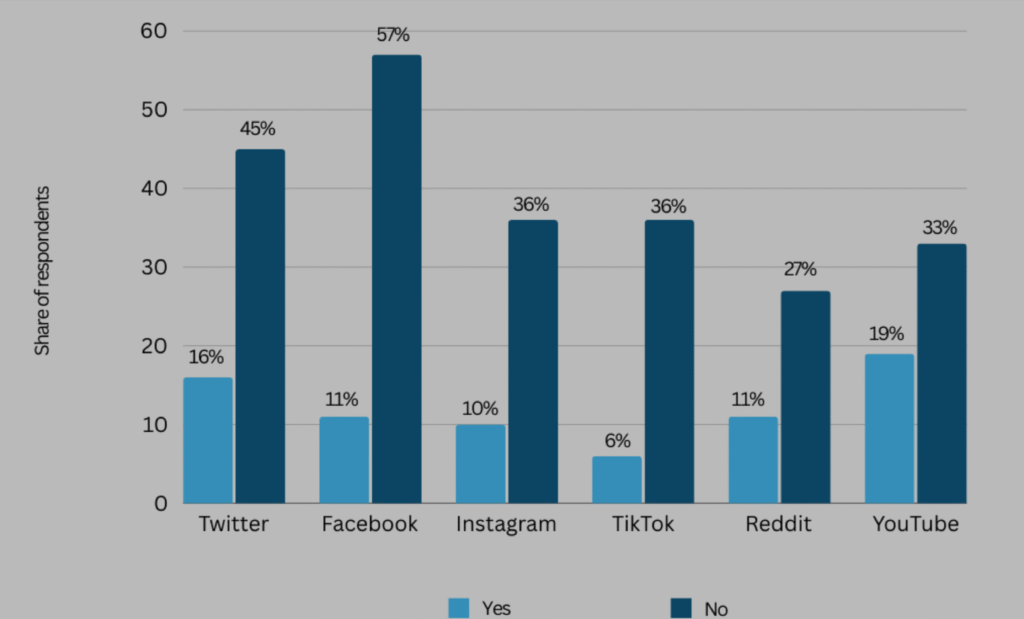
43. About 67% of Americans have said they have encountered false news in the media in one way or another. According to Statista, 52% of UK-based people come across false news daily. Occasionally, 34% come across false news,95% do not come across, and 5% do not know.
44. At least 44% of worldwide news readers have received false news in print media. According to a survey, 51% of global news readers have come across false news in one way or another.
45. 87% of Americans have come across false news on social networks. 10% of adults in the US have shared false news in one way or another, while 55% believe that false news on social network accounts is responsible for the spread of fake news.
46. About 1-3 of US citizens have mistakenly shared false information on social networks. According to the study, 38.25% of respondents believed that they had shared false news on social networks.
47. About 43% of news readers believed that social network firms managed false news well. 4 out of 10 adults in the US are fulfilled when social media firms use computer programs to find false news by using AI-powered tools to flag and remove fake news.
48. On Instagram, AI algorithms evaluate the text, images, and videos in user-generated content by detecting and removing risky information. In 2019, about 900 Facebook and Instagram accounts were banned for the alleged use of misleading practices to push trump narratives.
49. 42% of US adults are more worried about how accurate the news on social networks is. 24% of adults in the US are concerned about the accuracy of false news, and 13% said they are not bothered by it. About 12% are not worried about how accurate the news they come across in the media is, while only 9% have an opinion.
Fake News Dispersal Through News Networks

50. 44% of news readers don’t trust old-style news sources. About 51% of millennials believe they do not trust old-style news sources. Only about 61% of adults in the US trust the nation’s news, while 71% trust local news. Thus, 84% of news readers get information from reviews and stories that are said to be true before they post. Source Deloitte, Statista.
51. About 70% of US citizens believed that false news had eroded their trust in the government. The increase in the spread of fake political news in the media is alarming, especially during the election. According to research, unsure voters are more likely to vote for Trump in the 2016 election if the fake news about Hillary Clinton was believed.
52. About 40% visit 65 fake sites from social networks compared to 10% visit US new sites. Based on a study in 2017, the Economic Journal believed that social media drives more users to fake sites than real ones. This leads to the quick spread of fake political news. As of the 2016 presidential election, about 20 false stories got more views, likes, and shares than real stories. During the election, false news recorded 8.7 million engagements, whereas the actual stories only received 7.3 million.
53. 93% of videos online are AI-generated. According to an FBI report in 2017, some unknown persons created false online profiles for fake reporters and generated articles using AI. Some print and media outlets have published these fake articles for people to read. These profiles had images and cooked-up stories that increased the genuineness of persons who were never in existence. The FBI further said that in 12-18 months, there will be an increase in content manipulations and cyber criminality, which will lead to more false news worldwide.
Conclusion
These statistics show how fake news can easily spread, especially on the internet, which has about 5.6 billion daily users. The spread of false information can be risky and have many health implications. It misleads and can also threaten factual news sources. Fake news has become increasingly disturbing worldwide. However, teaching internet users and news readers how to identify fake news will help curb the menace.
FAQS
Given the increasing size of digital content and the independent nature of truth in many situations, dictating the precise amount of factual information online is very challenging. However, based on studies, we may conclude that only 50% of some information on the internet is true.
Another survey from the Center for Communication Policy, founded in 2003, suggests that 47.3% of the information in the media today is fake and variable. Most false news was in online sources like political blogs, Wikipedia, and social media. Most false news was also found on social media, where people participated the most.
About 70% of US citizens believed that false news had eroded their trust in the government.
About 67% of people on Facebook come across fake news, and some other social media pages, like websites, have 65% fake news, YouTube 56%, and television 51%.
The rise of false news is becoming significant, especially in this period of information from the media. According to statistics, 30% of Americans believe in half-truths, while 70% separate them from the actual truth.
